The BNMA BN Repository
This repository is a resource for posting and downloading Bayesian network models for sharing with others and for providing supporting material for publications. Please respect authors' rights where noted.
Search
8 BNs found.
Thermostat A
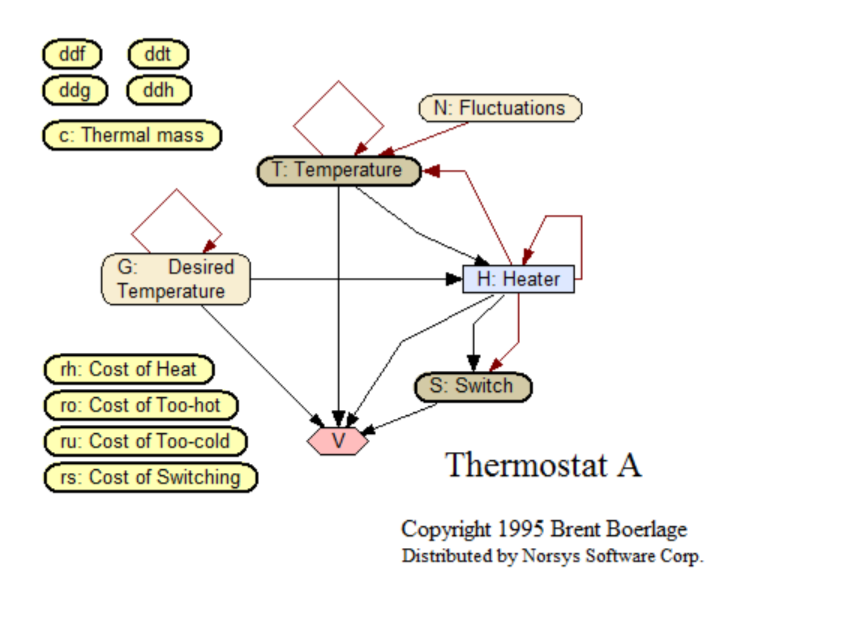
A time delay decision network for the thermostat-heater control problem. This is a simple example of heater control, with a single heater, single thermal mass, single sensor, and costs for overheating, underheating, energy and switching the heater on and off. It could easily be expanded into a more complex example.
Separable 2
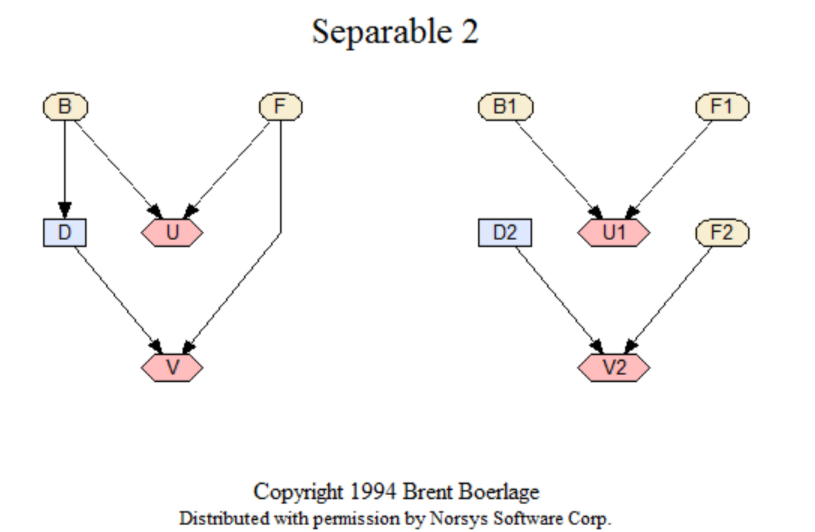
A simple example of a separable (termed 'abnormal' by Zhang) decision net, and the 2 nets it can be separated into. See Separable1 for an even simpler example. This network shows only dependencies, and does not include any numerical relationships.
BN link: <www.norsys.com...>
Separable 1

The simplest example of a separable (termed 'abnormal' by Zhang) decision net, and the 2 nets it can be separated into. This network shows only dependencies, and does not include any numerical relationships.
BN link: <www.norsys.com...>
Monty Hall Decision Problem
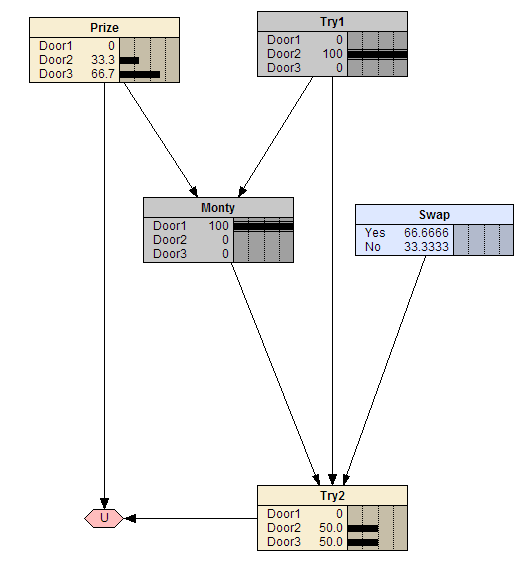
The Monty Hall problem (see <en.wikipedia.org...>) is a simple counter-intuitive puzzle. There are three doors, two of which have goats behind them and third door, a car. First, you pick a door. Monty then chooses a door with a goat behind it. Now it is up to you: Stay with your door or swap to the other unopened door?
Waterhole Fence
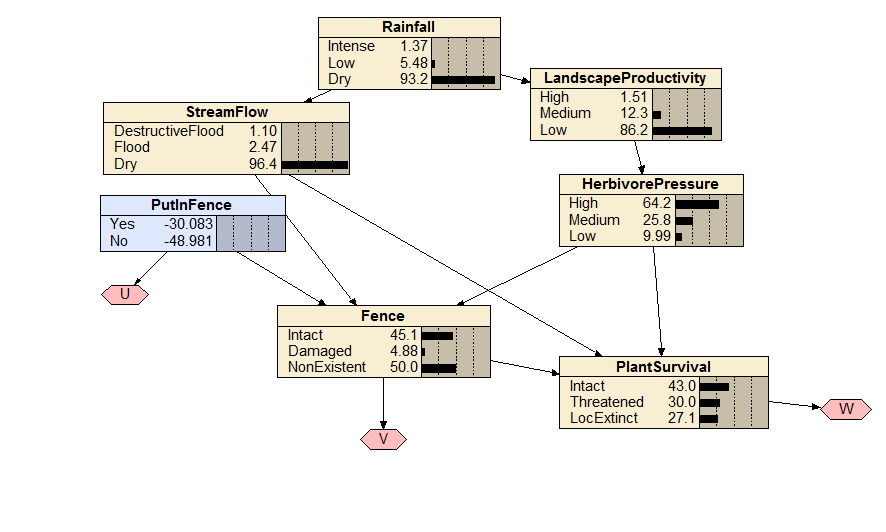
An assessment of the expected value of putting in a fence to promote plant survival, in the face of factors that affect the durability of the fence.
Go Surfing?
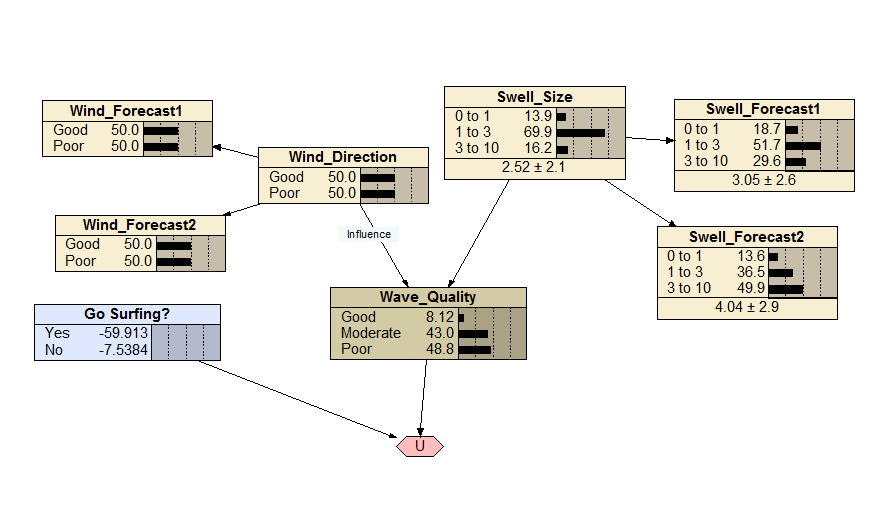
An example decision network for the dilemma of whether or not one should go surfing. The expected value of heading into the surf (or remaining put) is dependent on the wave quality, which is in turn dependent on wind direction and swell size. Both the wind direction and the swell size can be (imperfectly) forecast, and examples of handling these imperfect forecasts are included in the network.
Steroid Use Check
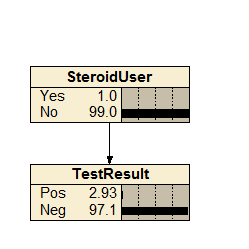
An extremely simple 2-node example demonstrating how true positive/false positive cases can be handled, in this case as applied to a steroid use test.
Illgraben Decision Graph
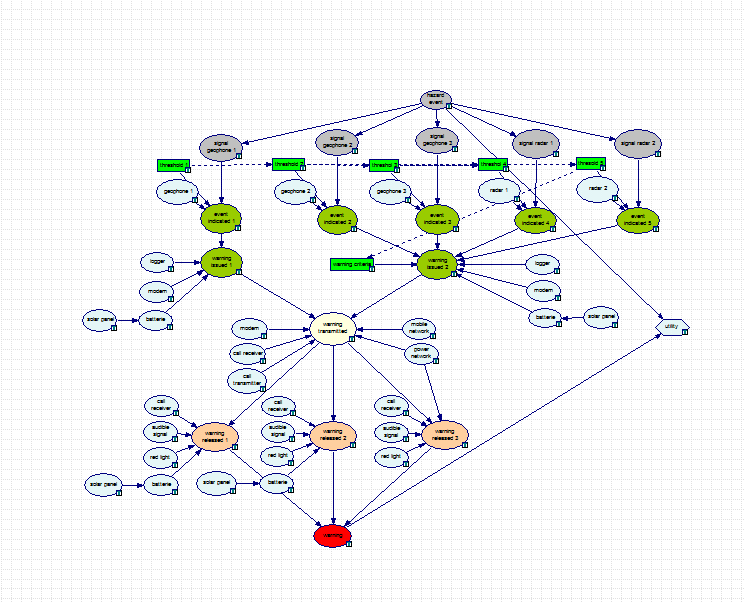
The Decision Graph is applied for the assessment and optimization of an existing threshold-based debris flow warning system. To model the warning system and compute the technical and inherent reliability, the Bayesian Network, which is the Decision Graph without the utility node, can be applied alone. Paper: <www.era.bgu.tum.de...>.
 Bayesian Intelligence
Bayesian Intelligence