The BNMA BN Repository
This repository is a resource for posting and downloading Bayesian network models for sharing with others and for providing supporting material for publications. Please respect authors' rights where noted.
Search
2 BNs found.
Pathfinder
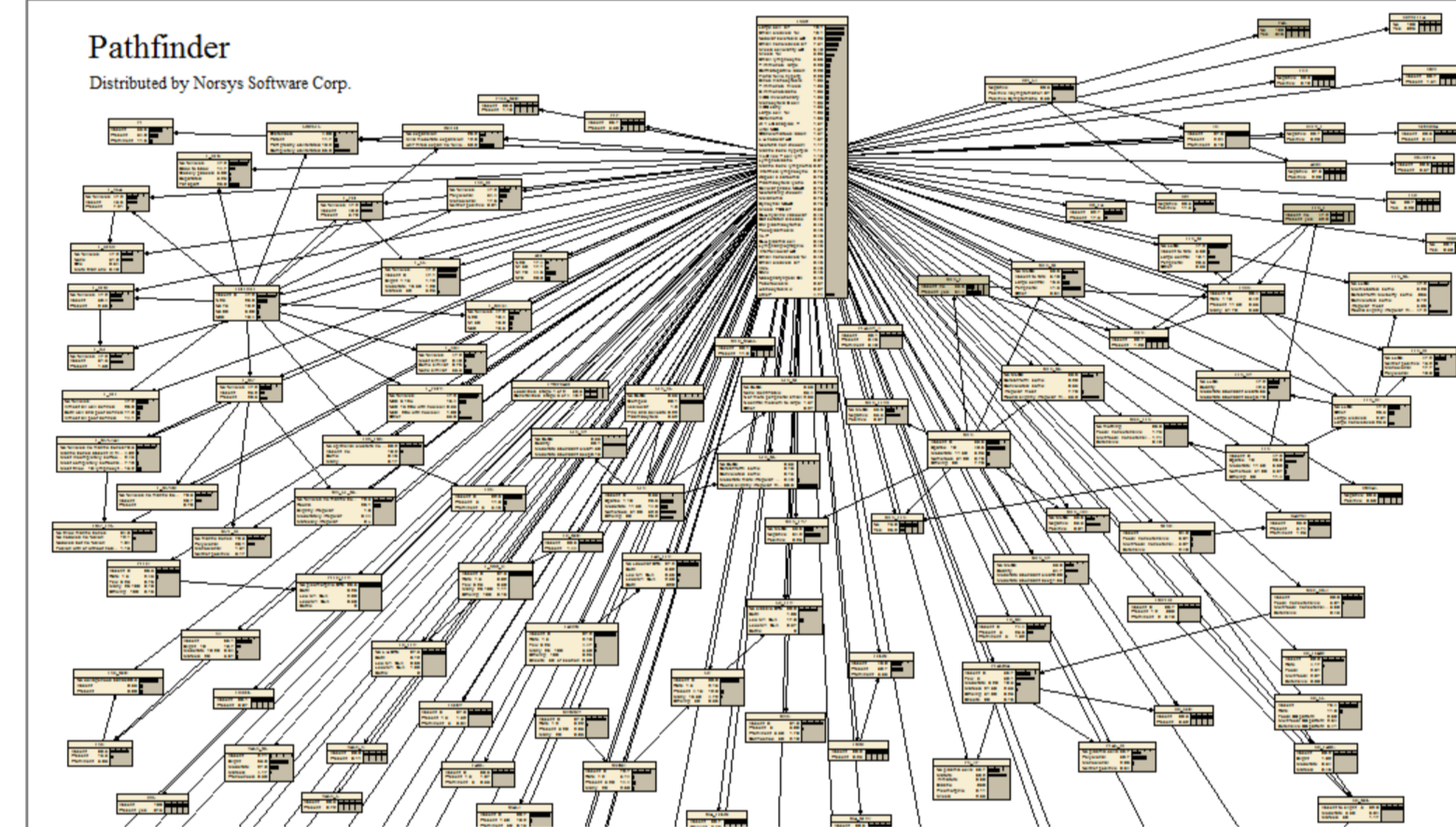
An expert system that assists surgical pathologists with the diagnosis of lymph-node diseases.
Paper link: <www.norsys.com...>
CC-BY-NC-ND
Netica .dne format
 Bayesian Intelligence
Bayesian Intelligence